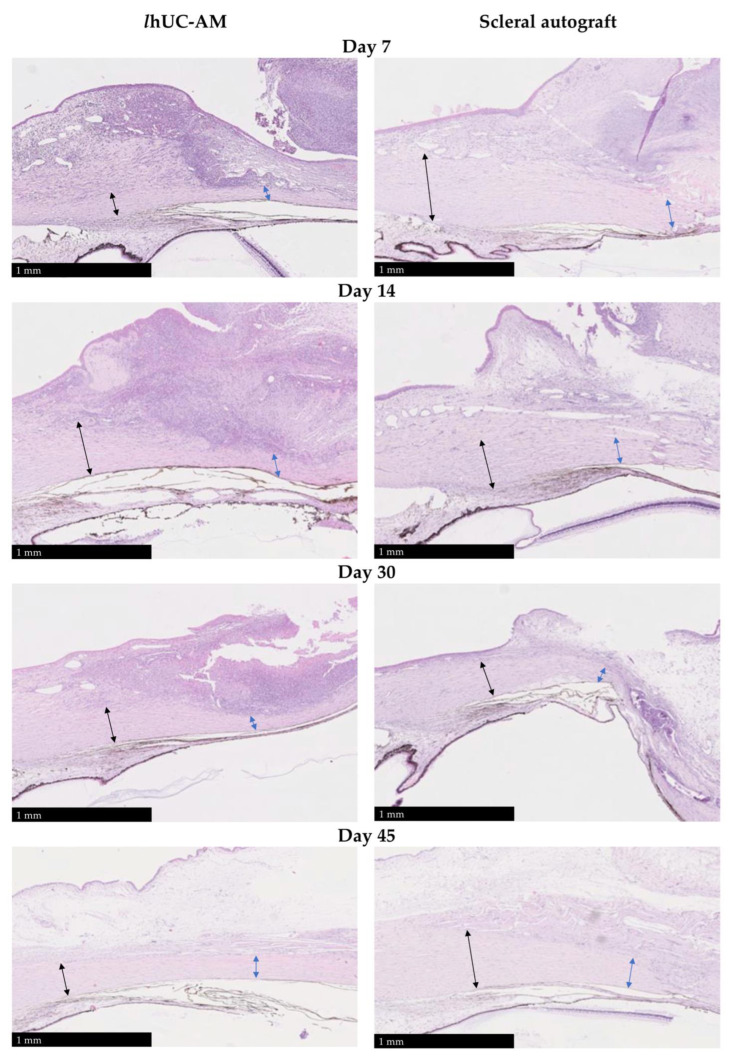
A preclinical study was performed to investigate the efficacy and safety of a new viral inactivated, devitalized, freeze-dried and gamma-sterilized human umbilical cord amniotic membrane (lhUC-AM) for the treatment of deep scleral and corneal defects with or without perforation. Firstly, lhUC-AM was investigated on experimental deep sclerectomy in rabbit eyes (n = 12) and compared to autograft (n = 4) on cross section histology. Secondly, lhUC-AM was studied on a selected series of uncontrolled cases of corneal defects (n = 18) with or without perforation, in dogs and cats. lhUC-AM tolerance, reconstruction of the deep corneal lesion and recovery of the structural aspect of the tissue were followed post-surgery. In experimental deep sclerectomy, histology showed that the lhUC-AM was well tolerated and degraded completely in 45 days while allowing an overall quality and kinetic of scleral regeneration, similar to autograft. In the clinical situations, lhUC-AM was well tolerated, with ocular inflammatory signs quickly decreasing after surgery. Mean follow-up was 16.40 ± 11.43 months. In 15 out of 18 cases, lhUC-AM allowed ocular surface wound healing. The ocular surface was fully reconstructed three months after surgery. This study suggests a good safety and efficacy profile of lhUC-AM in the treatment of deep corneal or scleral defect in animals. This new tissue should now facilitate the treatment of severe ocular surface diseases in humans.
Keywords: deep ocular defect, human umbilical cord amniotic membrane, placenta tissue, graft, sclera regeneration, corneal healing