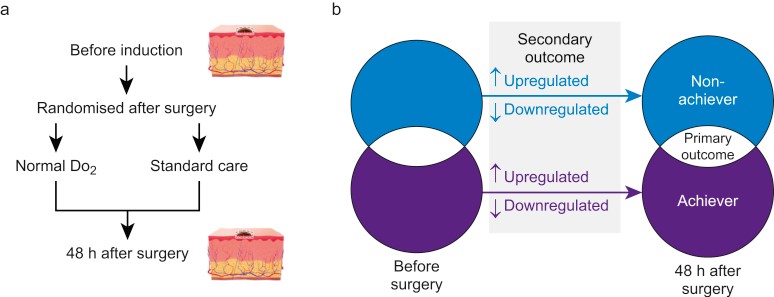
Background: Maintaining adequate oxygen delivery (DO2) after major surgery is associated with minimising organ dysfunction. Skin is particularly vulnerable to reduced DO2. We tested the hypothesis that reduced perioperative DO2 fuels inflammation in metabolically compromised skin after major surgery.
Methods: Participants undergoing elective oesophagectomy were randomised immediately after surgery to standard of care or haemodynamic therapy to achieve their individualised preoperative DO2. Abdominal punch skin biopsies were snap-frozen before and 48 h after surgery. On-line two-dimensional liquid chromatography and ultra-high-definition label-free mass spectrometry was used to characterise the skin proteome. The primary outcome was proteomic changes compared between normal (≥preoperative value before induction of anaesthesia) and low DO2 (<preoperative value before induction of anaesthesia) after surgery. Secondary outcomes were functional enrichment analysis of up/down-regulated proteins (Ingenuity pathway analysis; STRING Protein-Protein Interaction Networks). Immunohistochemistry and immunoblotting confirmed selected proteomic findings in skin biopsies obtained from patients after hepatic resection.
Results: Paired punch skin biopsies were obtained from 35 participants (mean age: 68 yr; 31% female), of whom 17 underwent oesophagectomy. There were 14/2096 proteins associated with normal (n=10) vs low (n=7) DO2 after oesophagectomy. Failure to maintain preoperative DO2 was associated with upregulation of proteins counteracting oxidative stress. Normal DO2 after surgery was associated with pathways involving leucocyte recruitment and upregulation of an antimicrobial peptidoglycan recognition protein. Immunohistochemistry (n=6 patients) and immunoblots after liver resection (n=12 patients) supported the proteomic findings.
Conclusions: Proteomic profiles in serial skin biopsies identified organ-protective mechanisms associated with normal DO2 after major surgery.
Clinical trial registration: ISRCTN76894700.
Keywords: oxygen delivery; proteomics; randomised controlled trial; sepsis; skin; surgery; wound infection.