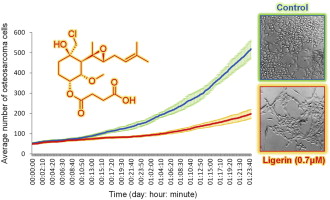
Ligerin (1) is a natural chlorinated merosesquiterpenoid related to fumagillin (2) exhibiting a selective antiproliferative activity against osteosarcoma cell lines and an in vivo antitumor activity in a murine model. Semisynthesis of ligerin analogs was performed in order to study the effects of the C3-spiroepoxide substitution by a halogenated moiety together with the modulation of the C6 chain. Results showed that all derivatives exhibited an in vitro antiproliferative activity against osteosarcoma cell lines and that chlorohydrin compounds were equally or more active than their spiroepoxy analogs. Among semisynthetic analogs, the parent compound 1 was the best candidate for further studies since it exhibited higher or equivalent activity compared to TNP470 (3) against SaOS2 and MG63 human osteosarcoma cells with a four times weaker toxicity against HFF2 human fibroblasts. Quantitative videomicroscopy analysis was conducted and allowed a better understanding of the mechanism of its antiproliferative activity.
Keywords: Antiproliferative; Cytostatic; Fumagillin; Ligerin; Marine-derived Penicillium; Osteosarcoma.