Utilization of patterned bioprinting for heterogeneous and physiologically representative reconstructed epidermal skin models
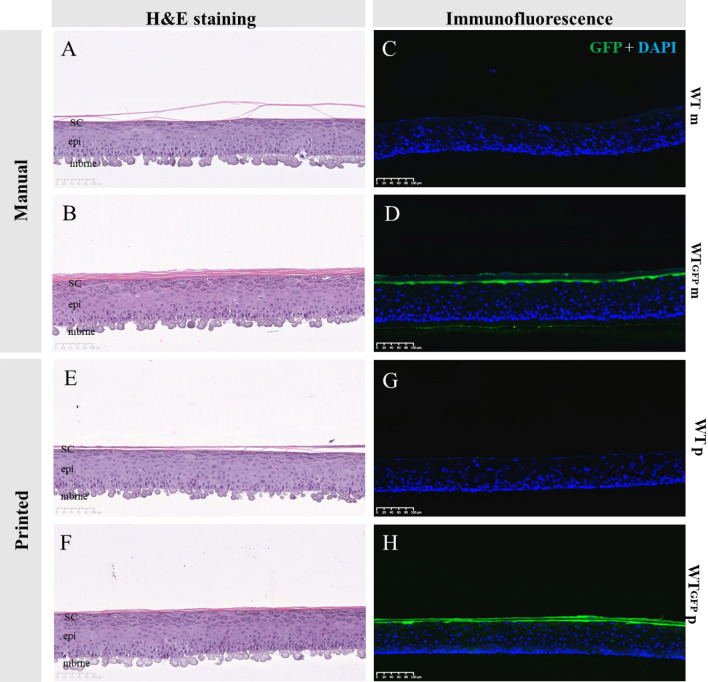
Organotypic skin tissue models have decades of use for basic research applications, the treatment of burns, and for efficacy/safety evaluation studies. The complex and heterogeneous nature of native human skin however creates difficulties for the construction of physiologically comparable organotypic models. Within the present study, we utilized bioprinting technology for the controlled deposition of separate keratinocyte subpopulations to create a reconstructed epidermis with two distinct halves in a single insert, each comprised of a different keratinocyte sub-population, in order to better model heterogonous skin and reduce inter-sample variability. As an initial proof-of-concept, we created a patterned epidermal skin model using GPF positive and negative keratinocyte subpopulations, both printed into 2 halves of a reconstructed skin insert, demonstrating the feasibility of this approach. We then demonstrated the physiological relevance of this bioprinting technique by generating a heterogeneous model comprised of dual keratinocyte population with either normal or low filaggrin expression. The resultant model exhibited a well-organized epidermal structure with each half possessing the phenotypic characteristics of its constituent cells, indicative of a successful and stable tissue reconstruction. This patterned skin model aims to mimic the edge of lesions as seen in atopic dermatitis or ichthyosis vulgaris, while the use of two populations within a single insert allows for paired statistics in evaluation studies, likely increasing study statistical power and reducing the number of models required per study. This is the first report of human patterned epidermal model using a predefined bioprinted designs, and demonstrates the relevance of bioprinting to faithfully reproduce human skin microanatomy.
Subject terms: Cell biology, Skin diseases, Tissue engineering